Dibutylamine CAS#111-92-2
CAS Number: 111-92-2
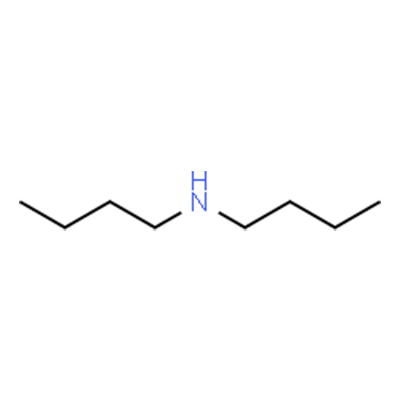
Chemical Formula: C8H19N
Synonyms:
(n-C4H9)2NH
1-Butanamine,N-butyl-
ai3-15329
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: Colorless Liquid
Dibutylamine CAS#111-92-2
Dibutylamine is a colorless liquid with anodor of ammonia. Molecular weight = 129.28; Boilingpoint = 159-161℃; Freezing/Melting point = - 61.9 to259℃; Flash point = 42-47℃; Autoignitiontemperature = 260℃. Explosive Limits: LEL = 1.1%;UEL—unknown. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA704 M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 2,Reactivity 0. Slightly soluble in water.
Dibutylamine Chemical Properties |
Melting point | −62 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 159 °C(lit.) |
density | 0.767 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
vapor density | 4.46 (vs air) |
vapor pressure | 1.9 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
refractive index | n |
Fp | 106 °F |
storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
solubility | water: soluble3.8g/L at 20°C |
form | Liquid |
pka | 11.25(at 21℃) |
color | White |
Odor | Weak ammonia. |
PH | 11.1 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
explosive limit | 0.6-6.8%(V) |
Water Solubility | 4.05 g/L (25 ºC) |
Merck | 14,3032 |
BRN | 506001 |
Dielectric constant | 3.0(20℃) |
Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, most common metals, strong acids. Vapours may flow over surfaces to a distant source of ignition. Can form explosive mixtures with air. |
InChI | 1S/C8H19N/c1-3-5-7-9-8-6-4-2/h9H,3-8H2,1-2H3 |
InChIKey | JQVDAXLFBXTEQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES | CCCCNCCCC |
LogP | 2.1 at 23℃ |
CAS DataBase Reference | 111-92-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Butanamine, N-butyl-(111-92-2) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Dibutylamine (111-92-2) |
Safety Information |
Hazard Codes | Xn,T |
Risk Statements | 10-20/21/22-35-23-21/22 |
Safety Statements | 45-36/37/39-28A-26-23 |
RIDADR | UN 2248 8/PG 2 |
WGK Germany | 1 |
RTECS | HR7780000 |
F | 10 |
Autoignition Temperature | 594 °F |
TSCA | TSCA listed |
HS Code | 2921 19 99 |
HazardClass | 8 |
PackingGroup | II |
Storage Class | 3 - Flammable liquids |
Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation |
Hazardous Substances Data | 111-92-2(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 550 mg/kg (Smyth) |
Product Application Of Dibutylamine CAS#111-92-2
Dibutylamine is a secondary dialkylamine. It is a versatile intermediate with a variety of applications.
Dibutylamine is extensively used in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling with aryl halides to synthesize arylamines, popularly known as Buchwald–Hartwig amination.
It can be used in the oxone-mediated annulation of 2-aminobenzamides and 1,2-diaminobenzenes to synthesize 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones and 1H-benzimidazoles, respectively.
It can also be used in the one-pot multicomponent reactions to synthesize tetra- and penta-substituted polyfunctional dihydropyrroles.
Dibutylamine was employed as organocatalyst during the synthesis of 2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromen-4-ylphosphonates via Knoevenagel, Pinner and phospha-Michael reactions. Di-n-butylamine (Dibutylamine) may be used to investigate the performance of a dry sampler, with an impregnated denuder in series with a glass fibre filter for airborne isocyanates. It was used in the preparation of 1M dibutylammonium phosphate buffer.
Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days