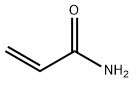
Acrylamide CAS#79-06-1
CAS Number: 79-06-1
Chemical Formula: C3H5NO
Synonyms:
ETHYLENECARBOXAMIDE
ACRYLAMIDE 2K
ACRYLAMIDE 4K
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: White Powder
Acrylamide CAS#79-06-1
Acrylamide is a white crystalline chemical substance and is a raw material for production of polyacrylamide. Solid acrylamide (abbreviated AM) is usually colorless and transparent flaky crystals with pure product being white crystalline solid which is soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, propanol, and slightly soluble in ethyl acetate, chloroform, and benzene. It can be hydrolyzed to acrylic acid in acidic or alkaline environment.
Acrylamide is a large class of the parent compound of monomers including methacrylamide, the AMPS (anionic monomer, 2-Acraylamide-2-Methyl Propane Sulfonic Acid), the DMC (cationic monomer, methyl-acryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) and N-substituted acrylamide compound.
Acrylamide Chemical Properties |
Melting point | 82-86 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 125 °C25 mm Hg(lit.) |
bulk density | 500kg/m3 |
density | 1,322 g/cm3 |
vapor density | 2.45 (vs air) |
vapor pressure | 0.03 mm Hg ( 40 °C) |
refractive index | 1.460 |
Fp | 138 °C |
storage temp. | 2-8°C |
solubility | 2040 g/L (25°C) |
pka | 15.35±0.50(Predicted) |
form | powder |
color | White |
Odor | Odorless solid |
PH | 5.0-7.0 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
Water Solubility | Acrylamide is routinely tested at 250 mg/mL in water, giving a clear colorless solution. It is soluble at least to 40% (w/v) in water, and reportedly up to 215 g/100 mL in water at 30°C. |
Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
Merck | 14,129 |
BRN | 605349 |
Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-9 atm?m3/mol): 3.03 at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
Exposure limits | Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: TWA 0.03, IDLH: 60; OSHA PEL: TWA 0.3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.03. |
Stability: | Unstable. Do not heat above 50C. Explosive. Incompatible with acids, bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, iron and iron salts, copper, aluminium, brass, free radical initiators. Air sensitive. Hygroscopic. |
Major Application | cleaning products |
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) | Acrylamide (79-06-1) |
InChI | 1S/C3H5NO/c1-2-3(4)5/h2H,1H2,(H2,4,5) |
InChIKey | HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES | NC(=O)C=C |
LogP | -0.9 at 20℃ and pH7 |
CAS DataBase Reference | 79-06-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Acrylamide(79-06-1) |
IARC | 2A (Vol. 60, Sup 7) 1994 |
EPA Substance Registry System | Acrylamide (79-06-1) |
Safety Information |
Hazard Codes | T |
Risk Statements | 45-46-20/21-25-36/38-43-48/23/24/25-62-48/20/21/22-22-24/25 |
Safety Statements | 53-45-24-36/37/39-26-36/37 |
RIDADR | UN 3426 6.1/PG 3 |
OEB | D |
OEL | TWA: 0.03 mg/m3 [skin] |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | AS3325000 |
F | 8-10 |
Autoignition Temperature | 424°C |
TSCA | TSCA listed |
HazardClass | 6.1 |
PackingGroup | III |
HS Code | 29241900 |
Storage Class | 6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 |
Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 3 Oral |
Hazardous Substances Data | 79-06-1(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in mice: 170 mg/kg (Peterson, Sheth) |
IDLA | 60 mg/m3 |
Product Application Of Acrylamide CAS#79-06-1
Over 90% of acrylamide is used to make polyacrylamides (PAMs), and the remaining 10% is used to make N-methylolacrylamide (NMA) and other monomers. Water treatment PAMs consumed 60% of the acrylamide; PAMs for pulp and paper production consume 20% of the acrylamide; and PAMs for mineral processing consume 10% of the acrylamide. Some of the specific uses of acrylamide are:
In liquid-solid separation where acrylamide polymers act as flocculants and aids in mineral processing, waste treatment and water treatment. They also help reduce sludge volumes in these applications.
As additives in the manufacture of paper and paper board products, leather and paint industries. In the paper industry PAMs act as retention aids during wet end processing and in wet strength additives.
In the manufacture of synthetic resins for pigment binders for textile/leather industries, and In enhanced oil recovery.
use in protein electrophoresis (PAGE), synthesis of dyes and copolymers for contact lenses. It is reasonably anticipated to be a hum an carcinogen.
Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days