Phytic acid CAS#83-86-3
CAS Number: 83-86-3
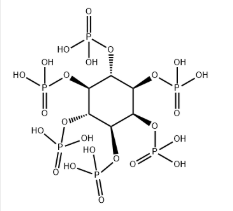
Chemical Formula: C6H18O24P6
Synonyms:
Alkalovert;Inositol hexaphosphoric acid, 40-50% aqueous solution
phyticacidsolution;sauredesphytins
Inositol hexaphosphoric acid, 40-50 wt% aqueous solution
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: White and yellow Liquid
Phytic acid CAS#83-86-3
Phytic acid (PA, molecular formula: C6H18O24P6, molecular structure is as follows ), also known as inositol hexakisphosphate, hexaphosphoinositol, myo-inositol hexakisphosphate, IP6, is pale yellow to pale brown slurry liquid, soluble in water, ethanol and acetone, nearly insoluble in ether, benzene and chloroform. It is stable and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents[1][2][3]. It’s basically non-toxic and should be sealed in a cool and dry place. Storage and transportation can be according to general chemical regulations.
PA first identified in 1855[4] is a naturally occurring compound formed during the maturation of seeds and cereal grains. It’s the storage form of phosphorus, an important mineral used in the production of energy as well as the formation of structural elements like cell membranes[5]. In the seeds of legumes, it accounts for about 70% of the phosphate content and is structurally integrated with the protein bodies as phytin, a mixed potassium, magnesium, and calcium salt of inositol[6].
PA is the most abundant form of phosphorus in plants. During food processing and digestion, inositol hexaphosphate can be partially dephosphorylated to produce degradation products, such as penta-, tetra-, and triphosphate, by the action of endogenous phytases, which are found in most PA-containing seeds from higher plants. Seed germination results in increased phytase activity, and PA hydrolysis releases phosphate and free myoinositol for use during plant development[6].
PA has the ability to bind minerals, proteins, and starch (either indirectly or directly). This binding alters the solubility, functionality, digestion, and absorption of these food components. At normal pH range, the phosphate groups of phytic acid are negatively charged, allowing interaction with positively charged components such as minerals and proteins. Metal ions may bind with one or more phosphate groups forming complexes of varying solubility. Proteins are able to bind directly with PA through electrostatic charges. Starch binding may also occur via hydrogen bond formation. Zinc appears to be the most affected by PA because it forms the most stable and insoluble complex. Other minerals and nutrients that are affected include calcium(Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), and chlorine (Cl)[4].
Phytic acid Chemical Properties |
Melting point | <25℃ |
Boiling point | 105 °C |
density | 1.432 g/mL at 25 °C |
vapor pressure | 0.039Pa at 60℃ |
refractive index | n |
storage temp. | 2-8°C |
solubility | Acetone (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Soluble) |
form | Colourless to Light Brown Solution |
pka | 1.13±0.10(Predicted) |
Specific Gravity | 1.282 |
color | Colorless to light yellow |
Odor | odorless |
Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
Merck | 14,7387 |
BRN | 2201952 |
Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | CHELATING |
InChIKey | IMQLKJBTEOYOSI-GPIVLXJGSA-N |
CAS DataBase Reference | 83-86-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
EPA Substance Registry System | myo-Inositol, hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate) (83-86-3) |
Safety Information |
Hazard Codes | Xi,C |
Risk Statements | 36/37/38-35 |
Safety Statements | 26-36-37/39-45-36/37/39 |
RIDADR | 1760 |
WGK Germany | - |
RTECS | NM7525000 |
TSCA | TSCA listed |
HazardClass | 8 |
PackingGroup | III |
HS Code | 29199000 |
Toxicity | LD50 intravenous in mouse: 500mg/kg |
Product Application of Phytic acid CAS#83-86-3
The most significant feature of PA is its strong complexation with metal ions and oxidation resistance[1][12], which makes it widely used.
In the food industry
Adding 0.05% to 0.1% phytic acid and sodium phytate to beverages and alcohols can remove the calcium, iron and copper heavy metal elements in beverages and alcohols which can protect the human body.
The preservative prepared with phytic acid sprayed on fruits and vegetables can effectively improve the fresh-keeping period. Proper addition of phytic acid as an antioxidant to vegetable oils or high-oil foods can extend the shelf life by 3 to 5 times.
Adding phytic acid to canned foods can achieve a stable color protection effect. Adding a trace amount of phytic acid to canned fish, shrimp, squid and other aquatic products can prevent the formation of struvite (glass-like ammonium magnesium phosphate crystal).
In the pharmaceutical industry
PA itself is a beneficial nutrient for the human body, which can promote the release of oxygen in oxyhemoglobin, improve the function of red blood cells, and prolong the survival of red blood cells. In addition, phytic acid is hydrolyzed in the human body to produce inositol and phospholipids. The former has anti-aging effects, and the latter is an important component of human cells. Phytic acid can relieve lead poisoning and can be used as a preventive agent for heavy metal poisoning. It can also prevent cancer and heart disease and can inhibit colon cancer and early breast cancer. Phytic acid can bind to iron in the intestine which could reduce the free radical production and inhibit cancer[5][10].
In other industries
PA can complex with metal ions bound to the surface of magnesium alloy to form a conversion coating, which can improve the resistance of magnesium alloy towards corrosion[13].
PA is a heat and light stabilizer, a flame retardant and an antistatic agent. The incorporation of a trace amount of phytic acid in the resin can maintain light and heat stability for a long time, and can effectively prevent self-agglomeration. It can be used as a hydrogen peroxide storage stabilizer as it can prevent the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. It can also be used as an antistatic agent for liquid fuels and fibers, as an anti-explosive additive for aviation gasoline, and as an excellent flame retardant for cotton, polyester, and silk fabrics.
Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days