Hydroxyapatite CAS#1306-06-5
CAS Number: 1306-06-5
Chemical Formula: Ca5HO13P3
Synonyms:
sodiumborate,monohydrate
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: White Solid
Hydroxyapatite CAS#1306-06-5
Calcium hydroxyapatite has a unique structure in that it is conductive along the hydroxide channels. OH- ions lie at (1/4/,1/4,1/4) and (3/4/,3/4,3/4) on the c-axis and charge-carrying protons are responsible for the observed conductivities in M10(PO4)6(OH)2. The H+ migration between the electroattractive ion (O2) to give molecular H2O in matrix channels carries charge and the resulting conductivity.
The unit cell consists of two triangular prismatic subcells forming a rhombic prism with vertical sides. There are two horizontal mirror planes at the OH levels of 1/4 and 3/4 of the c-axis. In addition, there is a center of inversion exactly in the center of each vertical face of each subcell.
Hydroxyapatite Chemical Properties |
Melting point | 1100 °C(lit.) |
density | 3.076 g/cm3(Temp: 18 °C) |
storage temp. | 2-8°C |
solubility | H2O: 0.3 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
form | solid |
color | White |
Water Solubility | insoluble H2O [MER06] |
Merck | 13,3500 |
Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | BULKING |
InChI | InChI=1S/2Ca.H3O4P.H2O/c;;1-5(2,3)4;/h;;(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q2*+2;;/p-4 |
InChIKey | CGMRCMMOCQYHAD-UHFFFAOYSA-J |
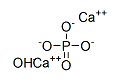
SMILES | [Ca+2].[Ca+2].P([O-])([O-])([O-])=O.[OH-] |
CAS DataBase Reference | 1306-06-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Hydroxylapatite (Ca5(OH)(PO4)3) (1306-06-5) |
Safety Information |
Hazard Codes | Xi |
Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
Safety Statements | 26-36 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | MY8434000 |
F | 3-10 |
TSCA | TSCA listed |
HS Code | 28352600 |
Storage Class | 13 - Non Combustible Solids |
Hazardous Substances Data | 1306-06-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Product Application of Hydroxyapatite CAS#1306-06-5
In the 1970s, it was found that sintered calcium hydroxyapatite, (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 (abbreviated as CaHap), possessed excellent biocompatibility and nontoxicity with femur and mandible bones. Since then, CaHap has been used as a biomaterial for artificial teeth and bones and as a filler for cements and polymers. Today, bone fillers made of CaHap are widely used in the medical and dental fields. In the 1980s, it was found that sintered CaHap has a good compatibility with skin tissues. Hence, percutaneous devices based on CaHap have been developed and applications have included continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and intravenous hyperalimentation systems, blood pressure measurement and blood access for nutrition. Recently, many researchers have studied the chemistry of apatites, particularly CaHap, and have found various applications, such as artificial teeth and bones, ion exchangers, adsorbents for chromatography to separate proteins and enzymes, catalysts, ionic conductors, temperature and gas sensors, etc.
Fact Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days