99.8% Acetic Acid CAS#64-19-7
CAS Number: 64-19-7
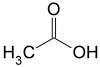
Chemical Formula: CH₃COOH
Synonyms:
Ethanoic acid
Ethylic acid
Methanecarboxylic acid
Vinegar acid
Appearance: Transparent liquid
HS Code: 2915211900
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Product Description – 99.8% Acetic Acid CAS#64-19-7
Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid or AcOH, is a key organic compound and the primary component responsible for the characteristic odor and taste of vinegar. It is one of the most important fatty acids, occurring naturally in many plants either in free form or as esters.
Chemical Formula: CH₃COOH
Appearance: Colorless, transparent liquid with a pungent odor and sour taste
Melting Point: 16.6 °C
Boiling Point: 117.9 °C
Relative Density: 1.049 (20/4 °C)
Solubility: Miscible with water, ethanol, glycerol, ether, and carbon tetrachloride; insoluble in carbon disulfide
Other Names: Ethylic acid, Methanecarboxylic acid, Vinegar acid, Glacial acetic acid
Glacial acetic acid refers to the anhydrous (water-free) form of acetic acid, which solidifies into ice-like crystals at low temperatures. It is corrosive and must be handled with care.
Acetic acid is a weak organic acid that exhibits the typical behavior of acids, including the ability to undergo esterification reactions with alcohols. Its production and usage date back thousands of years, with early records of vinegar brewing in ancient China. Modern concentrated acetic acid was first developed by Georg Ernst Stahl in 1700.
Parameters
Melting point | 16.2 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 117-118 °C(lit.) |
density | 1.049 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
vapor density | 2.07 (vs air) |
vapor pressure | 11.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
refractive index | n20/D 1.371(lit.) |
FEMA | 2006 | ACETIC ACID |
Fp | 104 °F |
storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
solubility | alcohol: miscible(lit.) |
form | Solution |
pka | 4.74(at 25℃) |
Specific Gravity | 1.0492 (20℃) |
color | colorless |
Odor | Strong, pungent, vinegar-like odor detectable at 0.2 to 1.0 ppm |
PH | 3.91(1 mM solution);3.39(10 mM solution);2.88(100 mM solution); |
PH Range | 2.4 (1.0M solution) |
Odor Threshold | 0.006ppm |
Odor Type | acidic |
explosive limit | 4-19.9%(V) |
Water Solubility | miscible |
λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 |
Merck | 14,55 |
JECFA Number | 81 |
BRN | 506007 |
Henry's Law Constant | 133, 122, 6.88, and 1.27 at pH values of 2.13, 3.52, 5.68, and 7.14, respectively (25 °C, Hakuta et al., 1977) |
Dielectric constant | 4.1(2℃) |
Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm ~25 mg/m3) (ACGIH, OSHA, and MSHA); TLV-STEL 15 ppm (37.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
Stability: | Volatile |
LogP | -0.170 |
CAS DataBase Reference | 64-19-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid(64-19-7) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid (64-19-7) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | C,Xi |
Risk Statements | 34-42-35-10-36/38 |
Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-23-24/25 |
RIDADR | UN 1792 8/PG 2 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | NN1650000 |
F | 1-8-10 |
Autoignition Temperature | 426 °C |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 8 |
PackingGroup | II |
HS Code | 29152100 |
Hazardous Substances Data | 64-19-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 in rats (g/kg): 3.53 orally (Smyth) |
IDLA | 50 ppm |
Product Application
Acetic acid is a large-scale industrial chemical and one of the most essential organic acids in the chemical industry. Its primary applications include the production of vinyl acetate, acetic anhydride, various acetates, and cellulose acetate. Vinyl acetate is a precursor for polyvinyl acetate, which is used in adhesives, films, and as a raw material for the synthetic fiber vinylon. Cellulose acetate is commonly utilized in the manufacturing of rayon and photographic film.
Esters of acetic acid with lower alcohols serve as excellent solvents and find wide usage in the coatings and paints industry. Additionally, acetic acid functions as a solvent in oxidation reactions, such as in the oxidation of p-xylene to terephthalic acid, a precursor to PET plastics.
In the organic synthesis sector, acetic acid is vital for producing acetic anhydride, diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, and halogenated acetic acids, as well as pharmaceutical intermediates like aspirin and agrochemicals like 2,4-D herbicide.
Acetic acid also plays a role in the manufacture of metal acetates (e.g., sodium, manganese, lead, aluminum, zinc, and cobalt salts). These compounds act as catalysts or additives in industries such as textile dyeing and leather tanning. For instance, aluminum acetate is used as a mordant and disinfectant in medical applications; lead acetate is a traditional pigment known as white lead; and lead tetraacetate is an oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis, particularly for converting 1,2-diols into aldehydes or ketones. Sodium acetate and potassium acetate are common buffering agents in biochemical applications.
In the food industry, acetic acid is used as an acidifier, flavor enhancer, and seasoning agent. For synthetic vinegar production, acetic acid is diluted to 4–5% concentration and combined with flavorings to mimic traditional vinegar. This method is cost-effective and time-efficient.
Note that acetic acid is highly corrosive, capable of causing skin irritation and blistering. It is classified as a Category 2 corrosive organic acid and must be handled with proper precautions.
Factory and Equipment Show
Delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days