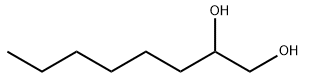
1,2-Octanediol CAS#1117-86-8
CAS Number: 1117-86-8
Chemical Formula: C8H18O2
Synonyms:
(R,S)-Octane-1,2-diol
R,S-Octane-1,2-diol
Octane-1,2-diol
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: Transperant Liquid
1,2-Octanediol CAS#1117-86-8
1,2-Octanediol has a variety of applications. It is used to improve HPLC separation of organic acids and bases and to synthesize halohydrin palmitates. Additionally, it is studied for its potential use as a pediculicide and has been shown to be effective against louse infestations. |
| 1,2-Octanediol Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 36-38 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 131-132 °C/10 mmHg (lit.) |
| density | 0.914 |
| vapor density | >1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.28Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.4505 (estimate) |
| Fp | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 3 g/L (20°C) |
| form | Low Melting Solid |
| pka | 14.60±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to white |
| Water Solubility | 3 g/L (20 ºC) |
| BRN | 1719619 |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | SKIN CONDITIONING - EMOLLIENT DEODORANT HAIR CONDITIONING SKIN CONDITIONING |
| LogP | 2.1 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1117-86-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,2-Octanediol(1117-86-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,2-Octanediol (1117-86-8) |
| Safety Information |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36 |
| Safety Statements | 37/39-26-24/25 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | IRRITANT |
| HS Code | 29053990 |
Product Application Of 1,2-Octanediol CAS#1117-86-8
Diols contribute to high water solubility, hygroscopicity and reactivity with many organic compounds, on usually linear and aliphatic carbon chain. 1,2-Octanediol, linear diol containing two primary hydroxyl groups, has bacteriostatic and bacteriacidal properties which are useful in cosmetics as a preservative. It is also used in coating materials, slurries, paper mills and water circulation systems for the effective preservation against bacteria and fungi. It is used as an emollient, humectant, and wetting agent in cosmetic and skin care products. Alcohols are very weak acids as they lose H+ in the hydroxyl group. Alcohols undergoes dehydration reaction which means the elimination of water molecule replaced by a pi bond between two adjacent carbon atoms to form alkenes under heating in the presence of strong acids like hydrocloric acid or phosphoric acid. Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones respectively. Carboxylic acids are obtained from oxidation of aldehydes. Oxidation in organic chemistry can be considered to be the loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen and reduction to gain hydrogen or loss of oxygen. Tertiary alcohols do not react to give oxidation products as they have no H attached to the alcohol carbon. Alcohols undergoes important reactions called nucleophilic substitution in which an electron donor replaces a leaving group, generally conjugate bases of strong acids, as a covalent substitute of some atom. One of important reaction of alcohol is condensation. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Almost infinite esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. Alcohols are important solvents and chemical raw materials. Alcohols are intermediates for the production of target compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, plasticizers, surfactants, lubricants, ore floatation agents, pesticides, hydraulic fluids, and detergents.
Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days