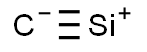Silicon carbide CAS#409-21-2
CAS Number: 409-21-2
Chemical Formula: CSi
Synonyms:
Silicon carbide -400 Mesh particle size, >=97.5%
carborun;silicon carbide, 400 grinding compound, 2oz
CARBORUNDUM BOILING CHIPS 4 MESH
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): 1 FCL (Full Container Load)
Appearance: White Powder
Silicon carbide CAS#409-21-2
Silicon carbide is a hard covalently bonded material predominantly produced by the carbothermal reduction of silica. Silicon carbide is made by heating silica sand and petroleum coke packed around electrodes in an electric resistance furnace to above 2200°C. Depending on the exact reaction conditions the resulting silicon carbide is either a fine powder or a bonded mass that requires crushing and milling to produce a usable feedstock. This material is very resistant to abrasion and to corrosion with a molten slag. It also has excellent resistance to thermal spalling. However as it is a carbide, it will oxidise readily, silicon carbide has a fairly high conductivity.
Several hundred structures of silicon carbide (polytypes) have been identified which have different stacking arrangements for the silicon and carbon atoms. The simplest structure is a diamond structure which is designated /3-SiC. Other structures are either hexagonal or rhombic and are referred to as a-SiC.
| Silicon carbide Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 2700 °C (lit.) |
| bulk density | 0.069g/cm3 |
| density | 3.22 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 2.6500 |
| solubility | Soluble in molten sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide and in molten iron. |
| form | nanopowder |
| color | Green |
| Specific Gravity | 3.22 |
| Resistivity | 107–200 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in molten alkalis (NaOH, KOH) and molten iron. Insoluble in water. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 1: no significant reaction with aqueous systems |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m |
| Merck | 14,8492 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 3 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 fiber/cm3 OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stability |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | ABRASIVE |
| InChIKey | HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Knoop Microhardness | 3000, at 25°C |
| Shear Modulus | 180 GPa, Calculated |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 459 - 476 GPa |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.14, sintered |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silicon monocarbide(409-21-2) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 111) 2017 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silicon carbide (409-21-2) |
| Safety Information |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| OEB | B |
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 (total) |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VW0450000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 28492000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 409-21-2(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Product Application of Silicon carbide CAS#409-21-2
Silicon carbide is one of the very few totally man-made minerals used in refractory work. These are:
Oxide-bonded-(S102, A1201, Si02 or silicate glass), silicon oxynitride (Si2 ON2), silicon nitride (S13N4)
The first three of these four bonding systems result in a permeable product, and when failure occurs in such masonry systems due to chemical degradation, it is usually due to attack on the bond. Thus, permeable units (where the corrodent penetrates the mass) are far more rapidly damaged.
Self-bonded”—(silicon carbide to silicon carbide) impermeable ones, where the attack is limited to the surface.
The self-bonded product can be manufactured by either of two methods: reaction bonded or sintered. Both will produce an impermeable unit, and they have roughly comparable chemical resistances, but they do not have identical physical properties.
Factory and Equipment Show
Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days